Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic
Adverse Reactions and Complications
Possible Allergic Reactions
Adverse reactions to Radiesse fillers can occur, and it’s essential to understand what they may be.
A possible allergic reaction to Radiesse fillers can cause a range of symptoms, from mild redness and swelling around the injection site to more severe reactions such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing.
These symptoms usually resolve on their own within hours or days after treatment, but in rare cases, they may persist for longer periods. In some instances, an allergic reaction can be life-threatening.
Complications related to Radiesse fillers include infection at the injection site, which can lead to redness, swelling, and pain that may require antibiotics or further medical attention.
Another possible complication is scarring, especially if the filler is not properly inserted or if there’s an allergic reaction. The filler material itself can cause skin irritation or a foreign body reaction in some individuals.
Other complications include the filler being dislodged or migrated, which can lead to unevenness or asymmetry in the treated area.
Nerve damage is another potential complication of Radiesse fillers, although it’s rare. The filler material can cause numbness, tingling, or pain around the injection site, and in severe cases, permanent nerve damage may occur.
Asymmetrical results are also a possible complication if the filler is not evenly distributed or if the correct amount is not used for the specific facial feature being treated.
Granulomas can form as a reaction to the filler material, causing raised bumps under the skin. This can be painful and may require removal by a doctor.
Serious complications such as embolism, thrombosis, or stroke are extremely rare but possible when using Radiesse fillers, especially in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or vascular problems.
Radiesse fillers can also cause more systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis, a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
Some patients may experience allergic reactions to Radiesse, including redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.
No serious adverse reactions to Radiesse have been reported, but some patients may experience more common side effects.
- Local reactions at the injection site: Redness, swelling, and itching can occur in some patients. These symptoms are usually mild and temporary, resolving on their own within a few days.
- Pain or tenderness: Some patients may experience pain or tenderness at the injection site, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain medication.
- Infection: As with any injectable treatment, there is a small risk of infection at the injection site. This is usually treated with antibiotics.
More serious complications can also occur, although they are rare.
- Necrosis or scarring: In rare cases, the Radiesse filler can cause necrosis (death) or scarring at the injection site. This is more likely to occur if the patient has a history of autoimmune disorders or is taking certain medications.
- Allergic reactions: Although rare, some patients may experience an allergic reaction to Radiesse, which can range from mild to severe.
- Systemic complications: There have been reports of systemic complications, such as swelling, redness, and itching, in some patients. These symptoms are usually mild and resolve on their own, but in rare cases, they can be more severe.
It is essential to note that these complications are extremely rare and that Radiesse has been approved by regulatory authorities worldwide for safe use.
Additionally, the manufacturer of Radiesse, Merz Aesthetics, has implemented measures to minimize the risk of adverse reactions, including conducting rigorous testing and monitoring for any potential side effects.
Patients who experience any unusual symptoms or complications after receiving Radiesse fillers should seek medical attention immediately.
Skin Necrosis and Scarring
To discuss the potential downsides of Radiesse fillers, it’s essential to delve into the possible adverse reactions and complications that can occur during or after treatment.
- Adverse Reactions:
- Complications:
- Skin Necrosis:
- Scarring:
- Risks and Contraindications:
- Long-Term Effects:
Some people may experience local irritation, swelling, redness, or inflammation at the injection site. In rare cases, more severe reactions such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing may occur.
Systemic reactions are also possible and can include fever, chills, or even anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
Common complications associated with Radiesse fillers include bruising, swelling, or bleeding at the injection site. In more severe cases, permanent scarring can occur if the filler material is not properly dissolved or removed.
Necrosis, or tissue death, can also be a complication of Radiesse injections. This occurs when the filler material causes damage to the skin and underlying tissues, leading to necrotic lesions or ulcers that require surgical intervention for repair.
Skin necrosis is a serious complication of dermal filler use, including Radiesse. It can occur as a result of several factors, such as improper injection technique, using too much filler material, or injecting into areas with poor blood supply.
The symptoms of skin necrosis may include painful ulcers, tissue death, and scarring that can lead to permanent disfigurement.
Permanent scarring is a potential complication of Radiesse fillers due to improper removal or dissolution of the filler material. This can result in noticeable scars or marks on the skin.
In some cases, scarring may be severe enough to require surgical intervention for repair, such as skin grafting or excision.
As with any medical treatment, Radiesse fillers carry risks and contraindications. Certain individuals should not receive Radiesse injections due to underlying health conditions or factors that may increase the risk of complications.
This includes people with bleeding disorders, autoimmune disorders, or those taking certain medications such as warfarin, aspirin, or ibuprofen.
The long-term effects of Radiesse fillers are not well understood and require further study. However, it’s essential to note that the filler material can remain in the body for several years, potentially causing ongoing problems such as scarring, inflammation, or tissue damage.
In rare cases, skin necrosis or scarring can occur due to the insertion of the filler needle or the introduction of the Radiesse particles into the dermis.
Necrosis and Scarring are potential complications associated with the use of Radiesse fillers.
- These complications can occur in rare cases, resulting from the insertion of the filler needle or the introduction of the Radiesse particles into the dermis.
- The skin necrosis or scarring may manifest as a red or swollen area at the injection site.
- In severe cases, necrosis and scarring can be persistent and lead to permanent damage.
These complications are generally more likely to occur in certain individuals, such as those with pre-existing skin conditions, weakened immune systems, or a history of keloid formation.
The risk of necrosis and scarring can also increase if the filler is not used correctly by an inexperienced practitioner or if it is over-filled or under-filled.
Additionally, Radiesse fillers can interact with other facial treatments or medications, such as botulinum toxin, hyaluronic acid fillers, or certain antibiotics, which may increase the risk of complications.
It’s essential to note that these complications are rare and typically occur in a small percentage of patients who receive Radiesse fillers.
However, it’s crucial for individuals considering Radiesse filler treatments to discuss their medical history, skin type, and any pre-existing conditions with their practitioner beforehand to minimize the risk of complications.
A thorough consultation and proper aftercare can help identify potential issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and minimizing the risk of long-term damage or scarring.
Systemic Reactions
An adverse reaction to Radiesse fillers can occur as a result of an allergic response, which can range from mild to severe. Mild reactions may include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site, while more severe reactions can cause hives, difficulty breathing, or even anaphylaxis.
Another potential complication of Radiesse fillers is a systemic reaction, also known as an allergic response or hypersensitivity reaction. This type of reaction occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to one of the ingredients in the filler, such as calcium hydroxylapatite. Systemic reactions can cause symptoms outside of the injection site, including fever, chills, nausea, and fatigue.
Systemic reactions can be categorized into three main types: Type I (immediate hypersensitivity), Type II (cytotoxic hypersensitivity), and Type III (immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity). Type I reactions are the most severe and occur within minutes to hours after injection, while Type II reactions occur within days to weeks after injection. Type III reactions can take several months to develop.
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions, also known as Type I reactions, are typically seen in people who have a history of allergies or sensitivities. Symptoms can include swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site, as well as more systemic symptoms such as hives, difficulty breathing, and rapid heartbeat.
Cytotoxic hypersensitivity reactions, also known as Type II reactions, occur when the body’s immune system identifies Radiesse filler particles as foreign objects. This can cause inflammation and damage to surrounding tissue, leading to complications such as scarring, lumpiness, or asymmetry in the treated area.
Immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, also known as Type III reactions, occur when the body’s immune system forms complexes between Radiesse filler particles and antibodies. These complexes can cause inflammation and damage to surrounding tissue, leading to complications such as scarring, lumpiness, or asymmetry in the treated area.
Other potential complications of Radiesse fillers include infection, which can occur when bacteria enter the injection site and cause an infection; granulomatous reaction, which is a type of inflammation that can cause scarring and damage to surrounding tissue; and necrosis, which is tissue death due to lack of blood supply.
Additionally, Radiesse fillers can cause chronic symptoms such as swelling, redness, or lumpiness at the injection site, even after the initial reaction has resolved. In rare cases, Radiesse fillers can also migrate from the injection site and cause complications such as asymmetry or scarring in other areas of the body.
It’s worth noting that the risk of adverse reactions to Radiesse fillers is relatively low, and most people who receive the filler do not experience any significant complications. However, it’s essential for individuals considering Radiesse fillers to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss any concerns with a qualified healthcare professional.
There have been reports of systemic reactions, including fever, chills, and difficulty breathing, although these are extremely rare.
Adequate medical supervision and aftercare are essential to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and complications associated with Radiesse fillers.
Serum-based dermal fillers, such as Radiesse, contain calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres that are designed to stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture. However, like all medical treatments, they can cause some degree of side effects in some individuals.
Adverse reactions to Radiesse fillers are typically mild and temporary, but in rare cases, they can be more serious. Systemic reactions have been reported, including fever, chills, and difficulty breathing, which can be life-threatening in severe instances.
Fever is a possible reaction to the filler particles or other components of the product, and it’s usually mild but may require antibiotic treatment if it persists or worsens. Chills can occur due to an allergic reaction or an immune response to one of the filler materials, and they’re often accompanied by other symptoms like redness, swelling, and warmth at the injection site.
Difficulty breathing is a rare but serious side effect that requires immediate medical attention. It’s thought to be caused by an anaphylactic reaction, which can also lead to swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, as well as a drop in blood pressure.
Other possible complications associated with Radiesse fillers include infection at the injection site, bleeding, bruising, and redness. In rare instances, an allergic reaction may occur, which can cause more severe symptoms such as hives, itching, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Some individuals may also experience changes in their facial anatomy after receiving Radiesse fillers, such as numbness, tingling, or a “frozen” sensation in the treated area. In rare cases, these symptoms can persist for weeks, months, or even years after treatment.
It’s worth noting that the risk of complications and adverse reactions is generally lower with Radiesse fillers compared to other dermal fillers on the market, such as hyaluronic acid-based products like Restylane or Juvederm. However, it’s essential for individuals considering filler treatment to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss their individual situation with a qualified healthcare professional.
Proper pre-treatment evaluation, informed consent, and post-injection care can significantly minimize the risk of adverse reactions and complications associated with Radiesse fillers. Individuals should always follow their doctor’s advice and attend scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor for any signs of problems or concerns.
Long-term Effects and Contraindications
Lack of Long-term Studies
The long-term effects and contraindications of *_Radiesse_* fillers, a type of collagen-based dermal filler, are not as well understood as those of other popular fillers such as *_hyaluronic acid_* or *_poly-L-lactic acid_*. As a result, the potential risks and side effects associated with long-term use of *_Radiesse_* have not been extensively studied, leaving patients and medical professionals alike to be cautious when considering this treatment option.
One of the main concerns surrounding long-term use of *_Radiesse_* fillers is their potential for *_granulomatous reaction_*, a rare but serious condition characterized by the formation of granulomas – inflamed tissue masses – in response to the filler material. This can lead to scarring, swelling, and other complications.
Another concern is the possibility of *_migration_* or *_extravasation_* of the filler material, where the collagen fibers break down and migrate out of the injection site, causing lumps, bumps, or irregularities in the treated area. This can be a difficult condition to treat, and may require multiple surgical procedures.
Reserve a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige
The long-term effects of *_Radiesse_* fillers on the body’s natural collagen production are also unknown. Some studies have suggested that repeated use of dermal fillers, including those made from collagen, may lead to an increase in the amount of collagen produced by the skin, which can result in a harder, more rigid texture.
There is limited research available on the long-term safety and efficacy of *_Radiesse_* fillers, making it difficult to determine whether they are safe for use over an extended period. The FDA has only approved *_Radiesse_* for short-term use, typically up to two years.
In terms of contraindications, *_Radiesse_* fillers may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as *_active bleeding_* or *_infection_* in the treatment area. Patients who are taking medications that affect blood clotting, such as *_aspirin_*, should also use caution when receiving *_Radiesse_* injections.
Additionally, patients who have had previous allergic reactions to collagen-based products may be more likely to experience an adverse reaction to *_Radiesse_* fillers. It is essential to discuss any medical history or allergies with a healthcare professional before undergoing treatment.
The lack of long-term studies on *_Radiesse_* fillers highlights the need for further research into their safety and efficacy. Until more information becomes available, patients should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks associated with this treatment option.
According to the FDA, there is limited data on the longterm effects of Radiesse, making it difficult to predict its safety and efficacy over time.
The long-term effects of Radiesse, a dermal filler made from calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres, are not well understood due to limited data available from the FDA. This lack of information makes it challenging to predict its safety and efficacy over extended periods.
According to the FDA, there is no long-term follow-up data on Radiesse to evaluate its effects after multiple years of use. Consequently, it is uncertain whether the fillers will continue to work as expected or if they may cause any adverse reactions in patients.
While some studies have shown that Radiesse can last for up to 2-3 years after treatment, these findings are based on limited sample sizes and short observation periods. It is essential to note that individual results may vary, and the duration of effectiveness may differ from person to person.
FDA reports also highlight concerns about the potential risks associated with repeated use of Radiesse or using high doses of the product. These concerns include the possibility of adverse reactions such as pain, swelling, redness, or bleeding at the injection site.
Furthermore, there is limited data on the interactions between Radiesse and other medications or medical treatments. Patients who are taking medications that can affect blood clotting should be cautious when undergoing Radiesse treatment, as this may increase their risk of developing complications such as bruising or hematoma.
In terms of specific contraindications, FDA-approved labeling for Radiesse lists certain conditions where the product is not recommended, including bleeding disorders, autoimmune disorders, and allergies to calcium hydroxylapatite or other components of the fillers.
Additionally, patients with active skin infections, skin cancer, or a history of keloid formation should avoid using Radiesse. The FDA also advises against using the product in areas with poor blood flow, as this may increase the risk of complications such as bruising or scarring.
More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and potential risks associated with Radiesse use. Until then, patients should carefully weigh the benefits and risks of treatment, and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider before undergoing dermal filler treatments.
The FDA will continue to monitor Radiesse for safety and efficacy as new data becomes available. In the meantime, it is crucial for medical professionals to inform their patients about the potential benefits and drawbacks of using this product for cosmetic or non-cosmetic procedures.
Contraindications
One of the significant long-term effects of Radiesse fillers is *foreign body rejection*, which can occur when the body’s immune system reacts to the _hyaluronic acid gel_ particles used in the filler. This can lead to the formation of nodules or lumps under the skin, which can be permanent.
Another long-term effect of Radiesse fillers is *granuloma formation*, where the body forms a mass of immune cells around the foreign particles. This can cause inflammation and scarring, and may require surgical removal of the filler.
The use of Radiesse fillers for facial rejuvenation also carries a risk of *_mask-like facelift_*, where the filler is not fully integrated into the surrounding tissue and appears unnatural or “masked” under the skin. This can be a temporary or permanent effect, depending on the individual’s response to the filler.
There are also concerns about the long-term effects of Radiesse fillers on *salivary glands*, as there have been reports of inflammation and swelling in these glands after injection. In some cases, this has led to long-lasting numbness or altered salivation patterns.
Another potential long-term effect is *_capsule formation_*, where the body forms a scar tissue capsule around the filler, which can lead to fibrosis and contracture of the surrounding skin.
Radiesse fillers are not suitable for everyone, and certain individuals should avoid treatment due to *contraindications*. These include:
– *_Active infections_* in the treated area, as this can increase the risk of complications such as abscesses or cellulitis.
– *_History of bleeding disorders_*, as Radiesse fillers are not suitable for individuals with conditions such as hemophilia or platelet dysfunction.
– *_Pregnancy or breastfeeding_* women, as there is limited research on the safety and efficacy of Radiesse fillers in these situations.
– *_History of allergic reactions_*, especially to _hyaluronic acid gel_, as this can increase the risk of anaphylaxis or other severe allergic responses.
– *_Autoimmune disorders_*, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, which may increase the risk of immune system reactions to Radiesse fillers.
– *_Skin conditions_*, such as eczema or psoriasis, which can increase the risk of complications and delayed healing.
It’s also essential to note that Radiesse fillers are not recommended for use in areas with *active keloid or hypertrophic scarring_* or *_poor wound healing_*, as these conditions may lead to complications such as further scarring or rejection of the filler.
Certain individuals are contraindicated from using Radiesse, including those with a history of bleeding disorders, autoimmune disorders, or previous adverse reactions to dermal fillers.
Radiesse fillers, composed of hyaluronic acid microspheres and calcium hydroxylapatite, are a popular choice for various cosmetic applications due to their efficacy and versatility. However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential long-term effects and contraindications to consider.
One significant concern is the risk of bleeding disorders. Individuals with a history of hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or other bleeding disorders should exercise extreme caution when undergoing Radiesse treatments, as the risk of excessive bleeding may be higher.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Autoimmune disorders are another contraindication for Radiesse use. Patients with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or scleroderma may experience an adverse reaction to the filler material, which can lead to inflammation and further exacerbate their underlying condition.
A history of previous adverse reactions to dermal fillers is also a contraindication for Radiesse. If you have had a severe allergic reaction or any other concerning response to a similar product in the past, it’s essential to disclose this information to your doctor before proceeding with treatment.
Additionally, certain medical conditions may increase the risk of complications associated with Radiesse treatments. These include autoimmune disorders affecting the skin and underlying tissues, as well as conditions that compromise blood clotting or vascular integrity.
The long-term effects of Radiesse fillers are still being studied and monitored by regulatory agencies and scientific communities worldwide. As a relatively new treatment option, there is ongoing research to fully understand its potential risks and benefits over extended periods of use.
One concern that has been raised is the possibility of implantation of foreign material under the skin. This risk is more significant for patients with compromised immune systems or those who have experienced previous adverse reactions to Radiesse.
Another consideration is the potential for filler migration or displacement over time, which may necessitate additional treatments or corrective procedures.
The interaction between Radiesse fillers and other medications is also an area of concern. Certain antibiotics, anticoagulants, or immunosuppressive agents may increase the risk of bleeding or interact with the filler material in unpredictable ways.
Finally, patients should be aware that Radiesse fillers are not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain anatomical characteristics or medical histories. Your doctor will carefully assess your individual situation and provide personalized guidance before recommending treatment.
Safety Concerns and Monitoring
Lack of Standardized Protocols
Safety concerns and monitoring are crucial aspects to consider when using Radiesse fillers. One of the significant risks associated with Radiesse is the potential for an allergic reaction, which can range from mild irritation to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- Any filler material carries a risk of infection or inflammation, especially in areas that are difficult to clean, such as the mouth or nose.
- The introduction of foreign substances into the body can also lead to granulomatous reactions, which involve an immune response and may require removal of the filler.
Monitoring for adverse reactions after Radiesse injections is essential. However, there is currently no standardized protocol for tracking and managing post-treatment complications.
A lack of standardization in monitoring protocols means that different clinics or practitioners may use varying methods to assess patient outcomes, which can lead to inconsistent results and inadequate care.
- There is a need for more research on the long-term effects of Radiesse fillers, as many studies have focused solely on short-term efficacy.
- The FDA requires that manufacturers report adverse events associated with their products, but there is no centralized registry for tracking filler-related complications.
A standardized protocol would enable clinicians to better identify and manage potential problems, improve patient outcomes, and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Additionally, a lack of standardization can lead to inconsistent product results, which may affect patient satisfaction and overall aesthetic outcome.
- The variability in clinical experience with Radiesse fillers means that some practitioners may not be aware of potential pitfalls or have the necessary training to handle complications effectively.
A more standardized approach to monitoring safety would help to ensure that patients receive consistent and high-quality care, and that clinicians can better manage any potential risks associated with Radiesse fillers.
There is currently a lack of standardized protocols for the use of Radiesse, which can lead to variability in treatment outcomes.
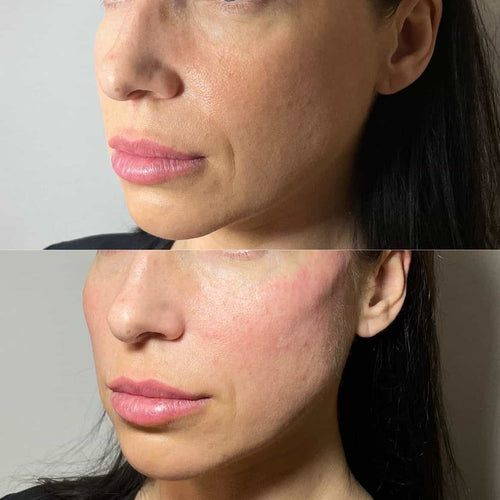
Safety concerns and monitoring are crucial aspects to consider when it comes to the use of Radiesse, a dermal filler composed of radioactive calcium hydroxylapatite particles.
One major safety concern with Radiesse is its potential for causing granulomas, which are abnormal growths that can occur in response to the foreign particles. These granulomas can be painful and may require surgical removal.
Another safety concern is the risk of scarring, particularly if the filler material is injected too close to the skin’s surface or if the patient has a history of keloid formation. In some cases, scarring can lead to permanent damage and affect the appearance of the treated area.
The use of Radiesse also carries a risk of infection, which can manifest as redness, swelling, or pus at the injection site. While this is rare, it’s essential for patients to report any signs of infection promptly to their healthcare provider.
Monitoring after treatment with Radiesse is critical to ensure that the filler has been successfully incorporated into the skin and that there are no adverse reactions. This typically involves regular follow-up appointments with a qualified healthcare professional.
A lack of standardized protocols for the use of Radiesse can lead to variability in treatment outcomes, as different providers may have varying approaches to injection technique, filler placement, and post-treatment care.
Some of the key concerns related to the standardization of Radiesse treatment include:
- Inconsistent injector training and experience
- Lack of clear guidelines for optimal filler concentration and needle size
- Variability in post-treatment care and follow-up schedules
- Insufficient data on long-term treatment outcomes and complications
Furthermore, the use of Radiesse may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with certain medical conditions, such as:
- Prior radiotherapy to the treated area
- Ectopic calcification or bone disease
- Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Immunosuppression or current use of immunosuppressive medications
It’s essential for patients to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks associated with Radiesse treatment and to discuss their individual concerns with a qualified healthcare professional.
Importance of Post-Procedure Care
The use of Radiesse fillers comes with several safety concerns and monitoring requirements to minimize the risks associated with their application.
Radiesse fillers are made from a type of calcium hydroxylapatite, a naturally occurring mineral found in the body. However, as with any medical procedure involving foreign substances, there is always a risk of adverse reactions, including redness, swelling, bruising, and pain at the injection site.
Additionally, Radiesse fillers can cause more severe complications, such as infection, scarring, or even an allergic reaction. In rare cases, the filler material may be absorbed too quickly, leading to the formation of granulomas or nodules under the skin.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to follow post-procedure care instructions provided by your doctor or dermatologist. This may include applying cold compresses or ice packs to reduce swelling and ease pain.
Monitoring the site for signs of infection or adverse reactions is also crucial. Your doctor may recommend regular check-ups or follow-up appointments to ensure that the filler is being tolerated well and to address any concerns.
The importance of post-procedure care cannot be overstated. Proper aftercare can significantly reduce the risk of complications, promote healing, and ensure optimal results from the filler treatment.
Furthermore, Radiesse fillers require regular maintenance to maintain their effectiveness over time. As with all fillers, the body may gradually absorb the material, causing the results to fade or decrease in effect.
This is why it’s essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations for touch-ups, revisions, or replacement treatments as needed.
Proper monitoring and post-procedure care also allow for early detection of any potential issues, enabling timely intervention and minimizing the risk of long-term complications.
It’s worth noting that some people may be more prone to adverse reactions from Radiesse fillers due to underlying medical conditions or medications. In such cases, careful monitoring and post-procedure care become even more critical.
Therefore, it’s essential to discuss any pre-existing conditions or concerns with your doctor before undergoing Radiesse filler treatment to ensure that you’re fully informed and prepared for the potential risks and benefits associated with this procedure.
In conclusion, while Radiesse fillers are a popular choice for facial rejuvenation, safety concerns and monitoring requirements cannot be ignored. By prioritizing post-procedure care and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can minimize the risks associated with this treatment and enjoy optimal results from your filler treatment.
Patients are advised to follow postprocedure care instructions carefully, including avoiding heavy lifting, rubbing, or strenuous activities, to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal results.
Certain side effects associated with *_Radiesse_* fillers, such as swelling, redness, and bruising, can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, cold compresses, and follow-up appointments with a qualified practitioner. However, some patients may experience more severe reactions, including an allergic reaction to the gel or particles.
In rare cases, *_Radiesse_* fillers have been associated with more serious complications, such as facial asymmetry, skin numbness, or eyelid swelling. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential risks and to carefully follow post-procedure care instructions to minimize the likelihood of complications.
Patients are advised to avoid *_heavy lifting_*, *_rubbing_* or *_strenuous activities_* for a specified period following treatment, as this can increase the risk of bruising or hematoma formation. Additionally, avoiding direct sunlight and wearing sunscreen with at least SPF 30 can help prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
A thorough medical history and physical examination are necessary to ensure that patients are suitable candidates for *_Radiesse_* fillers. Practitioners must also assess the patient’s overall health and monitor their response to treatment, as certain underlying medical conditions may impact the success or safety of the procedure.
During the follow-up appointment, a practitioner will assess the treated area for any signs of complications, such as bruising, swelling, or hematoma. In some cases, additional treatment may be necessary to resolve these issues and ensure optimal results.
Patients should also be aware that *_Radiesse_* fillers are not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions, such as *vascular disease*, *blood clotting disorders*, or *immune system disorders*. A qualified practitioner will carefully evaluate a patient’s individual risk factors and recommend alternative treatments if necessary.
In addition to monitoring for potential complications, practitioners should also educate patients on the importance of *_sun protection_* and *_smoking cessation_* after treatment. Both of these factors can impact the success and longevity of the results.
Regular follow-up appointments with a qualified practitioner are crucial to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of complications. By carefully monitoring patients and providing personalized care, practitioners can help them achieve their aesthetic goals while ensuring their safety and satisfaction.
Read more about Elizabeth Joy Photo here. Read more about Making Memories London here. Read more about Detailed Weddings LA here. Read more about Live Your Vows here. Read more about Crimson Hill here. Read more about One One Three Online here.
- Best CBD Infused Gummy Edibles For Winding Down After A Long Day - April 17, 2025
- Alluzience Longer Lasting Botox Near Ranmore, Surrey - April 16, 2025
- Why THC Beverages Are Gaining Popularity Among Millennials - April 12, 2025
